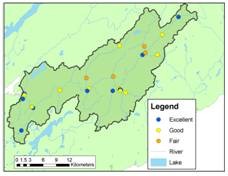
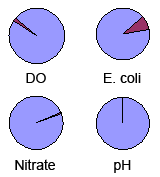
E. coli
E. coli is short for Escherichia coli, a type of bacteria. E. coli live primarily in the intestines of mammals and usually do not live long in the environment. The presence of E.coli is therefore used as an indicator of recent contamination by fecal matter, which may be of human or animal origin. Typical sources include wildlife, farm animals, and malfunctioning sewage systems (domestic or municipal). The presence of E.coli usually has little effect on the health of aquatic life, but may affect the suitability of the water for recreational use (such as swimming). This is why the results are compared to recreational use guidelines. Most E.coli is not itself hazardous to humans (with the exception of some less common strains) but the presence of E.coli indicates an increased risk that other more harmful pathogens may also be present.
Nitrate
Elevated concentrations of nitrate containing compounds can be harmful to aquatic life, and may contribute to excessive growth of algae or other aquatic plants. This may in turn lead to a variety of other adverse impacts including decreased oxygen levels and a reduction in biodiversity. When continued over time, this effect is termed eutrophication, an effect that can seriously affect the ecology and value of a water body. Major sources of excess nitrate in rivers and streams include fertilizer runoff from farm fields or domestic landscaping, runoff from manure piles, seepage from septic systems or malfunctioning sewage systems.
Eutrophication: build up of excessive nutrients which causes a dense growth of plant life, especially algae, which reduces the dissolved oxygen content, and often causes the extinction of other organisms.
pH
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the water. It affects how much other substances (such as metals) dissolve in the water. Many organisms that live in water are sensitive to changes in pH and may be adversely affected by pH that is either too high or low. The pH varies naturally depending on bedrock, climate and vegetation cover, but may also be affected by industrial or other effluents, the exposure of some kinds of rock (for example during road construction) or drainage from some mining operations.
Acid deposition ("acid rain") remains a concern in New Brunswick and may contribute to pH values exceeding guidelines in some areas. This is most likely to occur in watersheds with large proportions of acid-sensitive bedrock (such as granite) and in the south, where acid deposition is greatest.
Community Involvement
In this section, information is given on community groups or associations that are active in the protection and stewardship of the watershed and lists some of their main interests or accomplishments.
Common recreational and other uses of the watershed are also listed.
Summary
This section provides a summary of comments on the main findings of the water quality survey results. In cases where water quality did not meet all guidelines, information on the probable causes is given, if known.
Additional Information
This final section includes contact information to enable readers to obtain more detail on any item or to ask questions.